Nutrition
Welcome and thanks for visiting...

The Truth About Calories: Your Ultimate Guide to Healthy Eating and Weight Management

In a world overflowing with diet fads and conflicting nutrition advice, unraveling the truth about calories can feel daunting. Welcome to your ultimate guide on healthy eating and weight management, where we strip away the confusion and get to the core of what calories mean for your body. Understanding their role is essential not just for weight loss but for embracing a sustainable lifestyle that nourishes both mind and body. We’ll explore how the quality of the foods you consume can influence your overall health, debunk common misconceptions, and provide practical tips for making informed choices. Whether you’re aiming to shed a few pounds or want to feel better in your skin, this guide will empower you to take control of your eating habits and appreciate the balance between pleasure and nourishment. Prepare to unlock the truth about calories and set forth on a healthier, happier you!
Understanding Calories: What They Are and How They Work
Calories are more than just numbers on a nutrition label; they are fundamental units of energy that our bodies need to function. In scientific terms, a calorie is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius. This energy fuels everything we do, from the most basic physiological processes, like breathing and circulating blood, to more complex activities like exercising or even thinking.
But where did this concept come from?
The idea of calories as a measurement of energy originated in the 19th century through experiments involving a device called a bomb calorimeter. Imagine a small, sealed metal box—filled with food—submerged in a container of water. The food inside the box was ignited and completely burned, and the heat released from the combustion was absorbed by the surrounding water. By measuring how much the water's temperature rose, scientists were able to determine how much energy (or calories) the food contained. This process laid the foundation for how we understand the energy value of food today.

When we eat food, our bodies break it down into its basic components: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each of these macronutrients contains a specific number of calories per gram. Carbohydrates and proteins each provide four calories per gram, while fats are more energy-dense, offering nine calories per gram. These calories are then converted into energy through metabolic processes that support bodily functions and physical activities.
However, it’s essential to understand that not all calories are created equal. The source of these calories plays a crucial role in how they affect our bodies. Consuming 100 calories from a sugary soda will have a different impact on your health than 100 calories from a serving of vegetables. This difference is due to the presence of nutrients, fiber, and other beneficial compounds in whole foods, which can influence how your body uses and stores energy.
The Role of Calories in Weight Management
Calories are at the heart of weight management. The basic principle is straightforward: to maintain your weight, the number of calories you consume must equal the number of calories you burn. This balance is known as energy equilibrium. If you consume more calories than you burn, your body stores the excess energy as fat, leading to weight gain. Conversely, if you burn more calories than you consume, your body will use stored fat as energy, resulting in weight loss.
However, while the concept of energy balance is simple, the factors that influence it are complex. Your total daily energy expenditure (TDEE) includes several components: basal metabolic rate (BMR), the energy your body needs at rest to maintain vital functions like breathing and heartbeat; the thermic effect of food (TEF), the energy used to digest, absorb, and metabolize food; and physical activity, which varies widely among individuals. Understanding these components can help you better manage your weight.
Moreover, weight management is not just about the quantity of calories but also the quality. A diet high in nutrient-dense foods can help regulate appetite and energy levels more effectively than a diet high in empty calories. Foods rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats promote satiety and can prevent overeating. On the other hand, sugary and highly processed foods can lead to spikes and crashes in energy levels, increasing the likelihood of consuming excess calories.
Different Types of Calories: Good vs. Bad
The notion of "good" and "bad" calories is an oversimplification, but it can help illustrate the importance of food quality in a healthy diet. Good calories come from nutrient-dense foods that provide essential vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds. These foods support overall health, improve metabolic function, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Examples include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats like those found in nuts, seeds, and avocados.
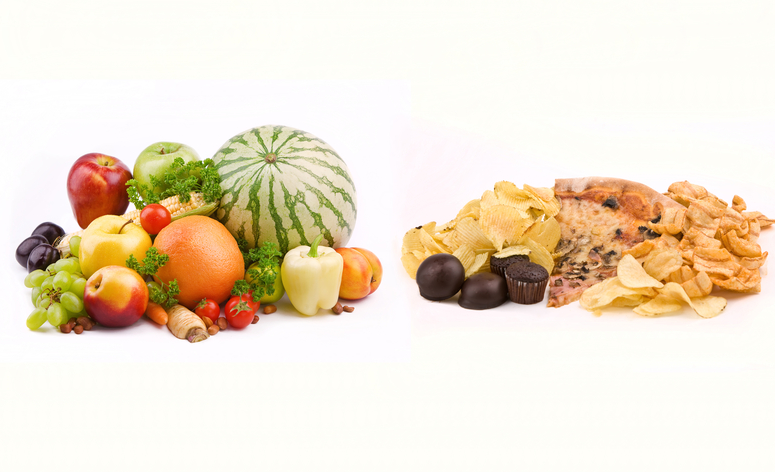

In contrast, bad calories are typically found in foods high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates. These foods are often referred to as "empty calories" because they provide energy but lack essential nutrients. Regular consumption of these foods can lead to various health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other chronic conditions. Examples include sugary beverages, fast food, sweets, and processed snacks.
It’s also worth noting that how food is processed and prepared can influence its caloric quality. Similarly, cooking methods like baking, grilling, and steaming preserve more nutrients compared to frying. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods and healthy preparation methods, you can ensure that the calories you consume contribute positively to your overall health.
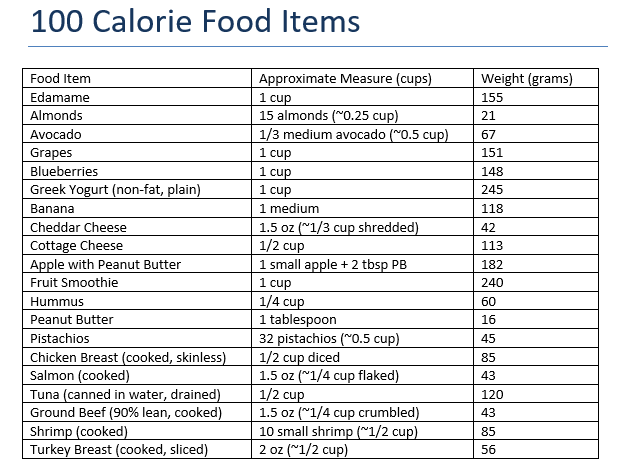
How to Calculate Your Daily Caloric Needs
Calculating your daily caloric needs involves understanding your body’s energy requirements. This can be done by determining your basal metabolic rate (BMR) and then factoring in your level of physical activity to estimate your total daily energy expenditure (TDEE). Several equations can estimate BMR, with the Harris-Benedict and Mifflin-St Jeor equations being the most commonly used.
The Harris-Benedict equation calculates BMR based on weight, height, age, and gender. For men, the equation is BMR = 88.362 + (13.397 x weight in kg) + (4.799 x height in cm) - (5.677 x age in years). For women, it is BMR = 447.593 + (9.247 x weight in kg) + (3.098 x height in cm) - (4.330 x age in years). The Mifflin-St Jeor equation is similar but slightly more modern and is often considered more accurate for contemporary lifestyles.
Once you have your BMR, you can calculate your TDEE by multiplying your BMR by an activity factor that corresponds to your level of physical activity. Sedentary individuals (little or no exercise) multiply by 1.2, lightly active individuals (light exercise/sports 1-3 days/week) by 1.375, moderately active individuals (moderate exercise/sports 3-5 days/week) by 1.55, very active individuals (hard exercise/sports 6-7 days a week) by 1.725, and extra active individuals (very hard exercise/sports & physical job) by 1.9.
By understanding your TDEE, you can tailor your caloric intake to meet your weight management goals. To lose weight, you would aim to consume fewer calories than your TDEE, creating a caloric deficit. To gain weight, you would consume more calories than your TDEE, creating a caloric surplus. For weight maintenance, your caloric intake should match your TDEE.
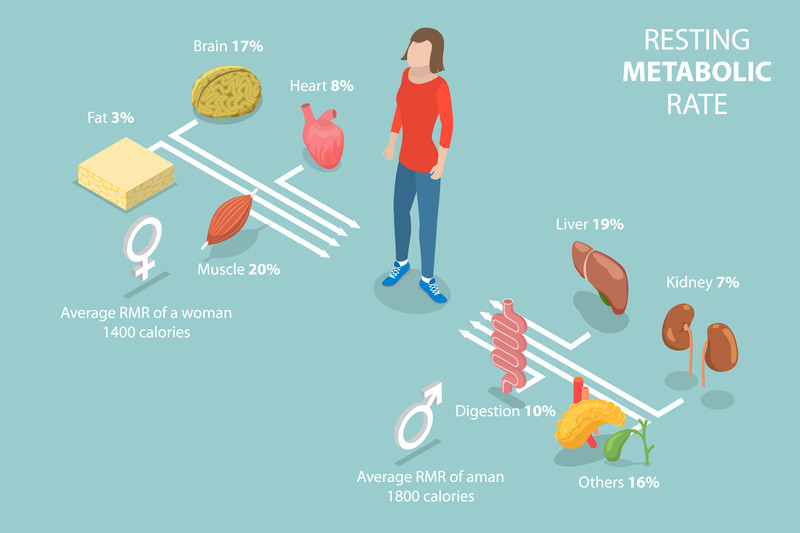
The Importance of Nutrient-Dense Foods
Nutrient-dense foods are vital for overall health and well-being. These foods provide high levels of essential nutrients relative to their calorie content. Examples include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Consuming a diet rich in nutrient-dense foods can help prevent nutrient deficiencies, support immune function, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Nutrient-dense foods are also beneficial for weight management. They tend to be more filling and satisfying than low-nutrient foods, which can help control appetite and prevent overeating. High-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, slow digestion and promote a feeling of fullness. Protein-rich foods, like lean meats, dairy, and legumes, also help regulate hunger by influencing appetite-regulating hormones.
In addition to their nutritional benefits, nutrient-dense foods can enhance the overall quality of your diet. They provide a range of flavors, textures, and colors that make meals more enjoyable and satisfying. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods, you can create a balanced and varied diet that supports physical and mental health.

Common Myths About Calories and Weight Loss
There are many myths and misconceptions about calories and weight loss that can make it difficult to navigate healthy eating. One common myth is that all calories are the same, regardless of their source. While it’s true that a calorie is a unit of energy, the nutritional quality of the food providing that calorie can significantly impact health and weight management. Nutrient-dense foods offer more health benefits and support better weight management than calorie-dense, nutrient-poor foods.
Another myth is that drastically cutting calories is the best way to lose weight. While creating a caloric deficit is necessary for weight loss, extreme calorie restriction can be counterproductive. It can slow metabolism, reduce muscle mass, and lead to nutrient deficiencies. Sustainable weight loss is best achieved through a moderate caloric deficit combined with a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
There’s also the misconception that certain foods, like grapefruit or celery, have "negative calories" and can promote weight loss by burning more calories during digestion than they provide. While some foods may have a very low calorie content and require energy to digest, the idea of negative-calorie foods is not supported by scientific evidence. Weight loss is best achieved through a balanced approach that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods.
Tips for Tracking Your Caloric Intake Effectively
Tracking your caloric intake can be a valuable tool for weight management, but it requires accuracy and consistency. One effective method is to use a food diary or a mobile app designed for calorie tracking. These tools can help you monitor what you eat, understand portion sizes, and identify patterns in your eating habits. Many apps also provide nutritional information and can help you set and track your caloric goals.
When tracking calories, it's important to be as precise as possible. This means measuring portions, reading nutrition labels, and accounting for all foods and beverages consumed. Estimating portion sizes or neglecting to track certain foods can lead to inaccuracies and undermine your efforts. Using a kitchen scale and measuring cups can help ensure that your portion sizes are accurate.
It’s also helpful to plan your meals and snacks in advance. This can prevent impulsive eating and help you stay within your caloric goals. Preparing meals at home allows you to control ingredients and portion sizes, making it easier to track calories. Additionally, being mindful of liquid calories from beverages like soda, alcohol, and coffee drinks is important, as they can add up quickly without providing satiety.
The Impact of Exercise on Caloric Balance
Exercise plays a crucial role in caloric balance and weight management. Physical activity increases the number of calories your body burns, which can help create a caloric deficit for weight loss or allow you to consume more calories while maintaining your weight. Different types of exercise, such as cardio, strength training, and high-intensity interval training (HIIT), can have varying effects on caloric expenditure.

Cardio exercises, like running, cycling, and swimming, are effective for burning a large number of calories in a relatively short amount of time. These activities elevate your heart rate and can improve cardiovascular health. The number of calories burned during cardio depends on the intensity and duration of the activity, as well as your body weight.
Strength training, which includes activities like weightlifting and bodyweight exercises, also contributes to caloric balance by increasing muscle mass. Muscle tissue burns more calories at rest compared to fat tissue, so increasing your muscle mass can boost your basal metabolic rate (BMR). This means you’ll burn more calories even when you’re not exercising. Strength training can also improve body composition and support long-term weight management.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) combines short bursts of intense activity with periods of rest or lower-intensity exercise. HIIT can be very effective for burning calories and improving metabolic health in a shorter amount of time compared to traditional cardio. Additionally, HIIT can create an "afterburn" effect, where your body continues to burn calories at an elevated rate after the workout is finished.
Check the online calories calculator
Healthy Eating Habits for Sustainable Weight Management
Developing healthy eating habits is key to sustainable weight management. One important habit is to focus on whole, unprocessed foods. These foods are typically more nutrient-dense and less calorie-dense compared to processed foods. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your diet can provide the essential nutrients your body needs while helping you feel full and satisfied.
Mindful eating is another effective habit for weight management. This involves paying attention to your hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly, and savoring your food. Mindful eating can help you become more aware of your eating habits and prevent overeating. It also encourages a positive relationship with food and can make meals more enjoyable.
Planning and preparing meals in advance can also support healthy eating habits. Having healthy meals and snacks readily available can reduce the temptation to eat unhealthy foods. Meal planning can help you stay within your caloric goals and ensure that you’re getting a balanced diet. Cooking at home allows you to control the ingredients and portion sizes, making it easier to manage your caloric intake.
Making Informed Choices for a Healthier Lifestyle
Unlocking the truth about calories is a journey toward understanding how energy intake and expenditure influence your health and weight. By recognizing the importance of nutrient-dense foods, debunking common myths, and applying practical tips for tracking calories, you can make informed choices that support a balanced and sustainable lifestyle.
Embracing a holistic approach to healthy eating and weight management means acknowledging that quality matters as much as quantity. It’s not just about the numbers but how those numbers translate into nourishing your body and mind. By prioritizing whole foods, engaging in regular physical activity, and developing mindful eating habits, you can achieve and maintain a healthy weight while enjoying a diverse and satisfying diet.
Remember, the goal is not perfection but progress. Small, consistent changes in your eating and exercise habits can lead to significant improvements in your overall health and well-being. Empower yourself with knowledge, listen to your body, and celebrate your journey toward a healthier, happier you.








