Health, Nutrition, Strength And Conditioning
Welcome and thanks for visiting...

Peptides Explained: What They Are and Their Role in Sports Performance

What Are Peptides?
Peptides are short chains of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. They play vital roles in various biological processes, including cell signaling, hormone production, and tissue repair. Unlike full proteins, peptides are smaller and more easily absorbed by the body, making them an attractive option for both medical and performance-enhancing purposes.
Think of peptides as cellular messengers—nature’s post-it notes—helping the body communicate quickly and efficiently. They activate pathways, transmit signals, and regulate essential cellular processes such as growth, metabolism, mood, appetite, and glucose management. Insulin, oxytocin, glucagon, and ghrelin are just a few examples of peptide hormones that serve as biological messengers, ensuring the body functions optimally.
Peptides occur naturally in all living species and can be unlocked from parent proteins using enzymes or microbes. A well-known example is lactoferricin, a peptide released from lactoferrin, a protein found in breast milk. When digested by infants, lactoferricin plays a critical role in supporting immunity. This illustrates how peptides provide targeted biological benefits precisely when and where they are needed.
In addition to endogenous peptides, scientific advancements have enabled the discovery of bioactive peptides from natural sources like plants and dairy. Advancements in AI-driven technology and machine learning have enabled scientists to analyze trillions of sequences, identifying novel bioactive peptides that enhance health and performance. This cutting-edge approach has led to groundbreaking discoveries in peptide science, with promising applications in sports and medicine.
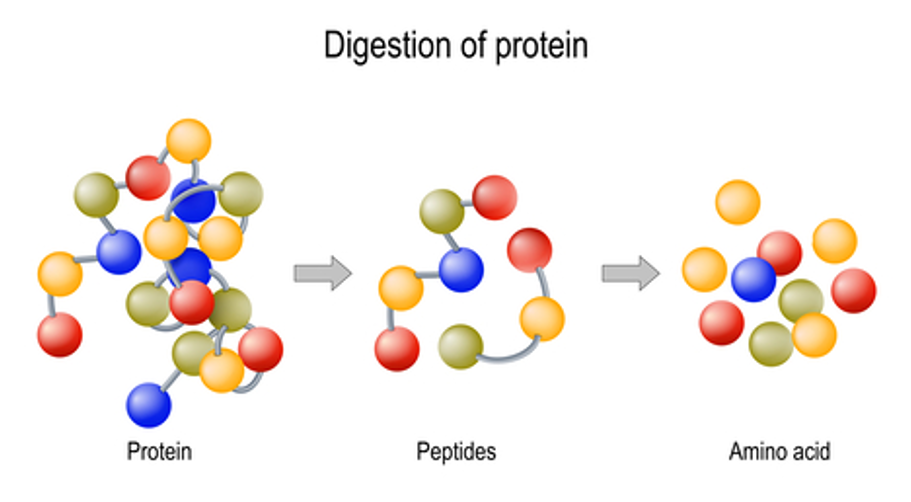
How Peptides Occur Naturally in the Body
Peptides are produced naturally in the body and serve various essential functions, including:
-
Hormonal Peptides: Some peptides act as hormones, regulating key bodily functions. Examples include insulin (blood sugar regulation), glucagon (glucose metabolism), and growth hormone-releasing peptide (GHRP) (stimulating growth hormone release).
-
Neurotransmitter Peptides: Certain peptides function as neurotransmitters, influencing brain activity and mood. Examples include oxytocin (the "love hormone") and endorphins (natural pain relievers).
-
Immune System Peptides: Peptides like thymosin alpha-1 enhance immune response, while defensins protect against infections.
-
Structural and Repair Peptides: Peptides contribute to tissue repair and growth. Collagen peptides are vital for skin, joints, and hair health, while BPC-157 promotes tissue regeneration.
-
Digestive and Metabolic Peptides: Peptides such as ghrelin stimulate hunger, while cholecystokinin (CCK) regulates digestion and appetite suppression.
-
Antioxidant Peptides: Peptides like glutathione protect cells from oxidative stress and aid in detoxification.
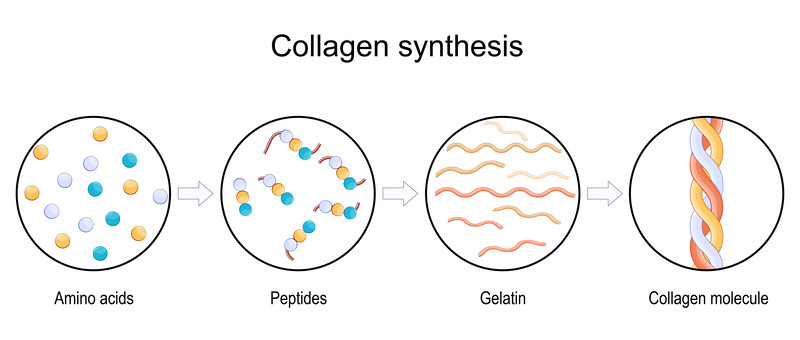
Natural vs. Synthetic Peptides
Peptides occur naturally in the body and can also be found in foods like eggs, milk, and soy. However, scientists have developed synthetic peptides to mimic or enhance the effects of naturally occurring ones. These synthetic versions are often designed for specific medical or performance-related applications, such as boosting growth hormone levels or accelerating injury recovery.
Additionally, bioactive peptides can be obtained through the enzymatic hydrolysis of proteins from natural sources, such as dairy, meat, and plant-based proteins. The method of extraction influences the effectiveness of these peptides, and enzymatic hydrolysis is one of the most efficient processes for enhancing their bioavailability and function.
What Is Enzymatic Hydrolysis? The Science Behind Biomolecule Breakdown
Enzymatic hydrolysis is a biochemical process in which enzymes break down complex molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, into smaller, more absorbable components. This reaction occurs naturally in digestion and is widely applied in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology. Unlike chemical hydrolysis, which relies on acids, bases, or heat, enzymatic hydrolysis is highly specific, operating under milder conditions with minimal unwanted byproducts. Enzymes such as proteases, lipases, and amylases target specific bonds, making the process efficient and tailored to desired outcomes. This method enhances bioavailability, digestibility, and functional properties in various applications, from producing protein hydrolysates in sports nutrition to improving food texture and flavor.

Source: Research Gate
Bioactive peptides are classified based on their functions, including:
-
Antihypertensive Peptides: Help regulate blood pressure by inhibiting angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE).
-
Antioxidant Peptides: Reduce oxidative stress and support cellular health.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides: Help the body fight against bacteria and viruses.
-
Immunomodulatory Peptides: Support immune system regulation and response.
-
Opioid Peptides Have pain-relieving properties similar to opioids but occur naturally in the body.
-
Satiety Peptides Influence appetite regulation and metabolism, helping with weight management.
-
Neuroprotective Peptides Aid in brain health and cognitive function, potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
-
Anticancer Peptides Some peptides have shown the potential to inhibit tumor growth and promote apoptosis in cancer cells.
Oral vs. Injectable Peptides
Peptides can be administered in two primary ways: orally or via injection.
-
Oral Peptides: They used to be generally less effective because peptides are broken down in the digestive system before they can reach the bloodstream. However, new technologies have improved their bioavailability.
-
Injectable Peptides: These are more effective as they bypass digestion, allowing direct absorption into the bloodstream. This might be a preferred method for performance-related uses, but it is more difficult to administrate.
Peptides and Sports Performance
AI-Driven Peptide Discovery: The Future of Muscle Health
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have transformed peptide research, enabling scientists to discover and optimize bioactive peptides that enhance muscle growth, recovery, and overall well-being. One of the most significant breakthroughs in this field is PeptiStrong™, developed through AI-driven peptide discovery by Dr. Nora Khaldi.

Derived from fava beans, PeptiStrong™ is a plant-based bioactive peptide that enhances muscle protein synthesis and reduces muscle breakdown at the cellular level. Unlike traditional protein supplements that rely on high protein intake, AI-designed peptides like PeptiStrong™ directly target specific muscle-building pathways, leading to faster recovery, greater muscle retention, and improved metabolic health.
Research highlights several key benefits of PeptiStrong™ compared to conventional protein sources:
- Increased Muscle Protein Synthesis – PeptiStrong™ stimulates muscle protein synthesis at a level comparable to whey protein, making it an effective plant-based alternative.
- Reduced Muscle Breakdown – It outperforms casein in preventing muscle loss, making it ideal for maintaining lean muscle mass.
- Faster Recovery After Training – Studies show PeptiStrong™ improves muscle strength recovery by 47%, allowing for more frequent and intense workouts.
- Lower Myostatin Levels – Since myostatin inhibits muscle growth, PeptiStrong™’s ability to reduce myostatin levels supports increased muscle retention.
- Natural and Plant-Based – As a fava bean-derived peptide, PeptiStrong™ provides a vegan-friendly alternative to traditional animal-based protein supplements.
By incorporating PeptiStrong™ into a structured nutrition and training regimen, athletes can experience enhanced muscle growth, superior recovery, and sustained energy levels—all while reducing the need for excessive protein intake.
Key Findings from Clinical Research:
-
Enhanced Muscle Protein Synthesis: A study published in the Journal of Nutrition demonstrated that PeptiStrong outperformed traditional milk protein in promoting muscle protein synthesis during recovery periods. nuritas.com
-
Improved Strength Recovery and Reduced Fatigue: Research featured in Nutrients revealed that PeptiStrong supplementation led to significant improvements in strength recovery and a reduction in muscle fatigue following intense exercise. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
Increased Strength and Bone Density: A recent clinical trial reported that participants experienced a 19.7% increase in strength and a 1% increase in bone density after 56 days of PeptiStrong supplementation.nuritas.com
Peptides and Their Functions in Sports
Beyond PeptiStrong™, bioactive peptides play a crucial role in athletic performance by supporting muscle repair, recovery, and endurance. The effectiveness of these peptides depends on their ability to remain intact and active after digestion and absorption. The table below summarizes key bioactive peptides, their sources, and their primary physiological effects based on recent research:
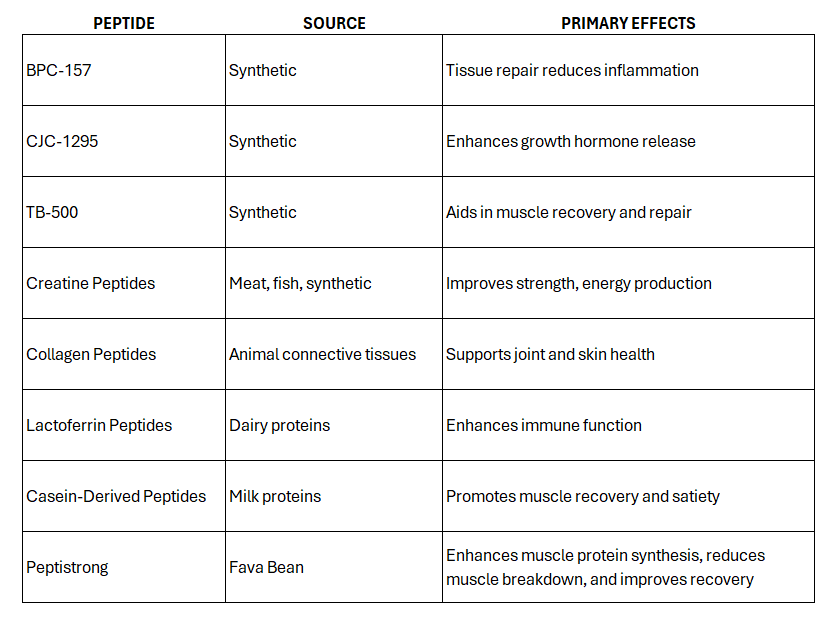
Moreover, research suggests that bioactive peptides can influence mitochondrial function, leading to enhanced energy production, reduced muscle fatigue, and improved oxygen delivery during high-intensity exercise. This makes peptides valuable for athletes and fitness enthusiasts seeking optimal performance and recovery.
Final Thoughts
Bioactive peptides and AI-driven research are revolutionizing muscle health and performance. Peptides like PeptiStrong, developed using AI to identify the most effective muscle-enhancing compounds, are setting new standards for scientifically validated supplementation. Unlike traditional protein supplements that require high doses and prolonged digestion, AI-optimized peptides offer superior bioavailability and targeted muscle support.
These advancements benefit athletes, aging adults, and fitness enthusiasts alike, helping to preserve and build muscle more efficiently. The growing body of research highlights the ability of bioactive peptides to accelerate recovery, enhance endurance, regulate inflammation, and support overall metabolic function—key factors in optimizing physical health and longevity.
With continuous progress in peptide extraction and formulation, natural bioactive peptides from dairy, meat, and plant-based proteins are becoming more potent and accessible. Their role in sports nutrition and medical applications is expanding, offering a safe and effective alternative to synthetic peptides, which require careful regulatory consideration.
As scientific understanding deepens, peptides will continue shaping the future of sports science and general wellness. By incorporating research-backed peptides into a balanced diet and training program, individuals can maximize their benefits for sustained performance, recovery, and overall well-being.
References
-
ScienceDirect – Bioactive Peptides and Their Functional Properties. Retrieved from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/food-science/bioactive-peptides
-
ScienceDirect – Peptide Therapeutics and Enzymatic Hydrolysis. Retrieved from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1756464619302233
-
ScienceDirect – Peptides and Their Role in Muscle Recovery and Performance. Retrieved from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0753332221010593?via%3Dihub
-
World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) – Guidelines on Peptide Use in Sports. Retrieved from: https://www.wada-ama.org
-
National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Peptide Research and Its Role in Medicine. Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
-
PubMed Central (PMC) – Research on PeptiStrong and Muscle Recovery. Retrieved from: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9967853/








